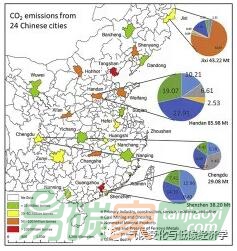
中國是世界上最大的能源消費國和二氧化
碳排放國。城市占中國二氧化碳排放總量的85%,因此城市被視為實施旨在適應氣候變化和減少二氧化碳排放的
政策的關鍵領域。然而,由于缺乏系統的統計數據以及現有數據質量較差,中國城市的排放清單建設尚未得到很好的研究。針對這一研究差距,作者基于能量平衡表制定了一套中國城市二氧化碳排放清單的方法。新建的排放清單是根據IPCC地區排放核算方法提供的定義編制的,涵蓋47個社會經濟部門,17個化石燃料和9種基礎工業產品,與國家和省級清單相對應。在這項研究中,作者應用這些方法編制了24個中國普通城市的二氧化碳排放清單,并檢查了清單的不確定性。了解中國城市的排放源是未來許多氣候政策和目標研究的基礎。
China is the world's largest energy consumer and CO2 emitter. Cities contribute 85% of the total CO2 emissions in China and thus are considered as the key areas for implementing policies designed for climate change adaption and CO2 emission mitigation. However, the emission inventory construction of Chinese cities has not been well researched, mainly owing to the lack of systematic statistics and poor data quality. Focusing on this research gap, we developed a set of methods for constructing CO2 emissions inventories for Chinese cities based on energy balance table. The newly constructed emission inventory is compiled in terms of the definition provided by the IPCC territorial emission accounting approach and covers 47 socioeconomic sectors, 17 fossil fuels and 9 primary industry products, which is corresponding with the national and provincial inventory. In the study, we applied the methods to compile CO2 emissions inventories for 24 common Chinese cities and examined uncertainties of the inventories. Understanding the emissions sources in Chinese cities is the basis for many climate policy and goal research in the future.
Shan, Yuli, Guan, Dabo, Liu, Jianghua, Mi, Zhifu, Liu, Zhu, Liu, Jingru, Schroeder, Heike, Cai, Bofeng, Chen, Yang, Shao, Shuai and Zhang, Qiang (2017) Methodology and applications of city level CO2 emission accounts in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 161. pp. 1215-1225. ISSN 0959-6526
