文章導讀
自20世紀70年代以來,海洋中的塑料碎片一直被認為是一大環境隱患。由于人類活動的影響,塑料會在其價值鏈的任意一點流失到環境中,還會經歷不同的
運輸和轉化過程。為有效減少塑料對海洋生態環境的影響,首先應該確定那些因人類活動而進入環境中的塑料總量。因此,本文從聚合物類型及其應用、地理區域和塑料的生命周期等角度全面的評估了環境中塑料的損失量。原文摘要海洋中的塑料污染
問題備受關注,因此迫切需要量化世界上塑料的環境損失,包括不同地理區域,不同聚合物類型,以及沿塑料價值鏈產生的損失。在這項研究中,我們使用現有文獻和數據庫以及經改進的量化損失方法模型,對全球整個塑料價值鏈中塑料的環境損失進行了估算,還進行了綜合的敏感性和不確定性分析,以確定塑料在環境損失方面的關鍵因素。總體上,我們發現,2015年大約有6.2 Mt(95%置信區間,CI:2.0-20.4 Mt)的大塑料和3.0 Mt(CI:1.5-5.2 Mt)的微塑料損失到環境中。大塑料主要來源于中低收入國家(4.1 Mt)城市垃圾管理不善。對于微塑料,主要來源是橡膠輪胎的磨損,道路標記的磨損以及城市揚塵中的塑料。為了遏制海洋塑料污染,需要像我們這樣的量化以評估塑料在不同來源和位置對環境造成的損失的程度,并能夠進一步評估其對環境的破壞。通過不確定性和敏感性分析,我們重點介紹了在進一步研究工作中應該優先考慮的塑料來源,以便更全面、準確地表示全球塑料損失。
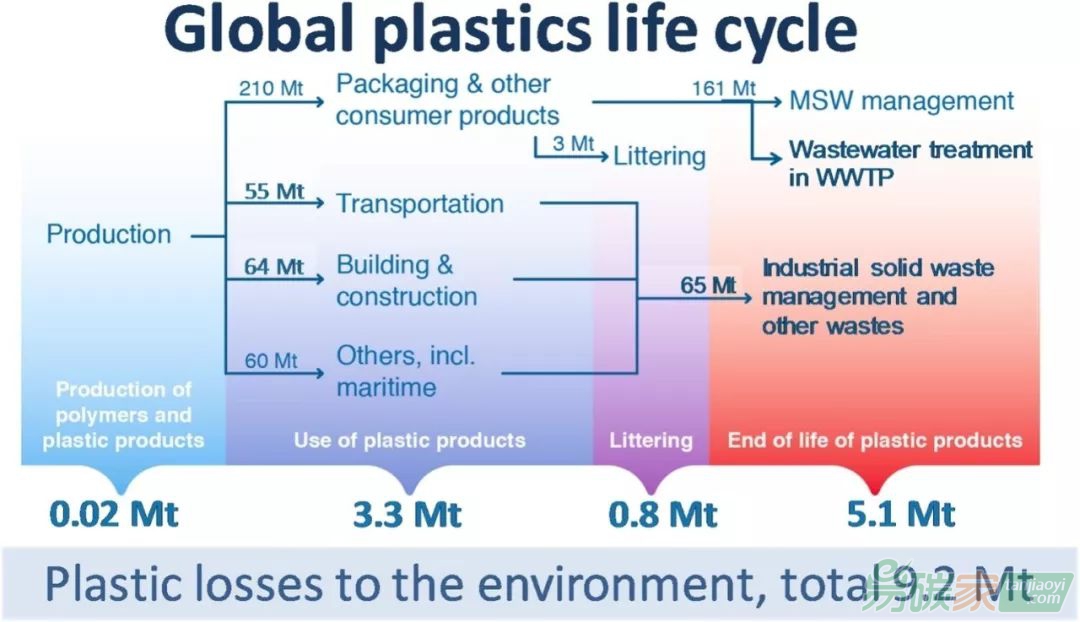
圖1 全球塑料價值鏈和2015年塑料在環境中的損失估計量
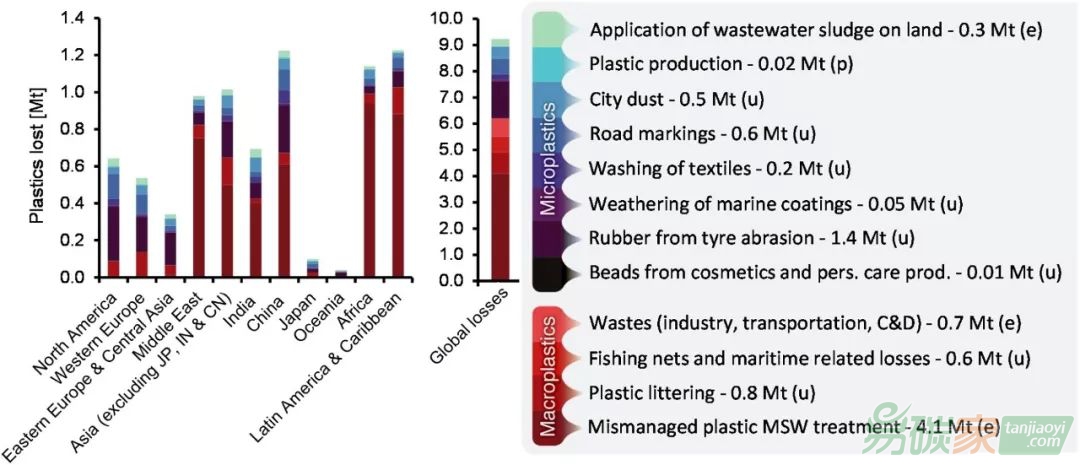
圖2 不同區域和來源的大塑料和微塑料的損失量
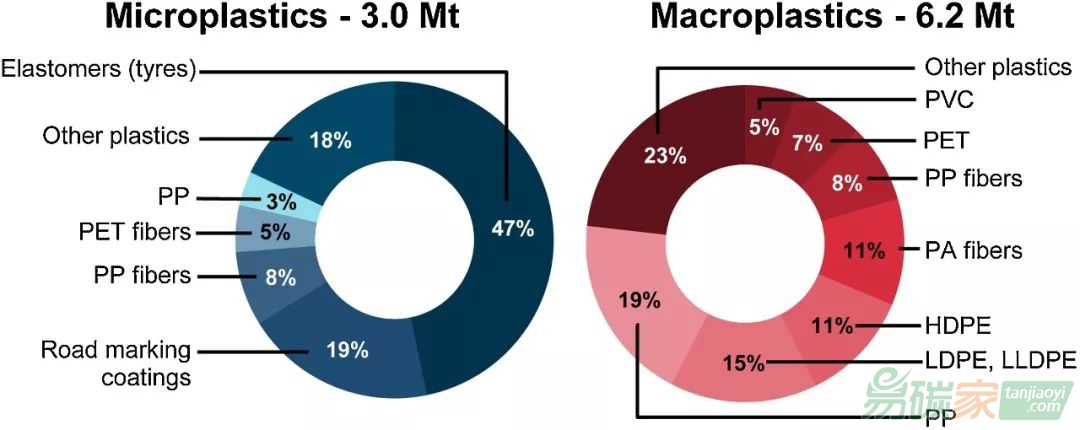
圖3 不同聚合物類型和應用的大塑料和微塑料的損失量
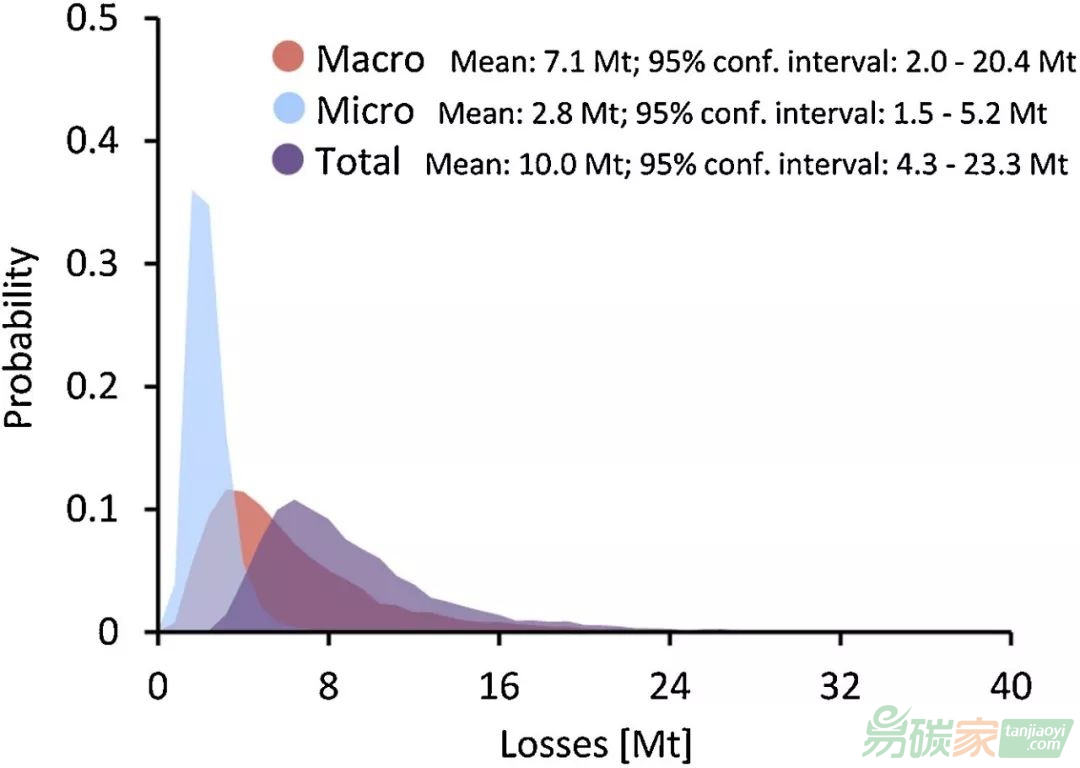
圖4 塑料損失的概率分布
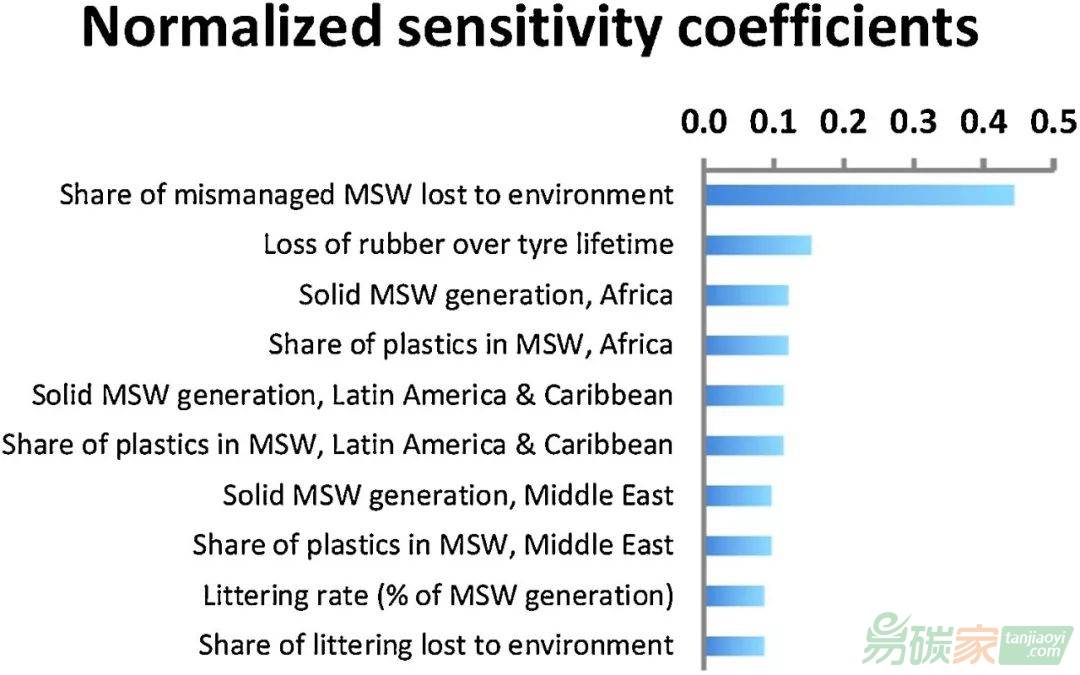
圖5 對塑料損失量最敏感的十個參數

原文信息

AbstractWith the increasing focus on marine plastic pollution, quantification of the environmental losses of plastics in the world, with differentiation into geographic regions, polymers and loss occurrences along the plastics value chains, is required. In this study, we make a global estimation of the losses of plastics to the environment across the entire plastic value chain, using existing literature and databases coupled with improved and additional methodological modelling of the losses. The resulting loss estimates are unprecedented in their detailed differentiations between polymers (23), plastic applications (13), geographical regions (11), and plastic value chain stages. Comprehensive sensitivity and uncertainty analyses were also conducted to identify key drivers in terms of plastic losses. We overall found that approximately 6.2?Mt (95% confidence interval, CI: 2.0–20.4?Mt) of macroplastics and 3.0?Mt (CI: 1.5–5.2?Mt) of microplastics were lost to the environment in 2015. The major macroplastic loss source was identified as the mismanaged municipal solid waste (MSW) management in low-income and lower-middle income countries (4.1?Mt). For microplastics, the major sources were abrasion of tyre rubbers, abrasion of road markings and plastics contributing to city dust generation. To curb marine plastic pollution, such quantified mapping as ours are needed to evaluate the magnitude of the plastics losses to environment from different sources and locations, and enable a further assessment of their environmental damage. Through our uncertainty and sensitivity analyses, we highlight plastics sources that should be prioritized in further research works to obtain a more comprehensive and accurate representation of global plastics losses.
本期編輯:劉盈,
北京林業大學環境科學與工程學院,碩士研究生,研究方向:產業生態學